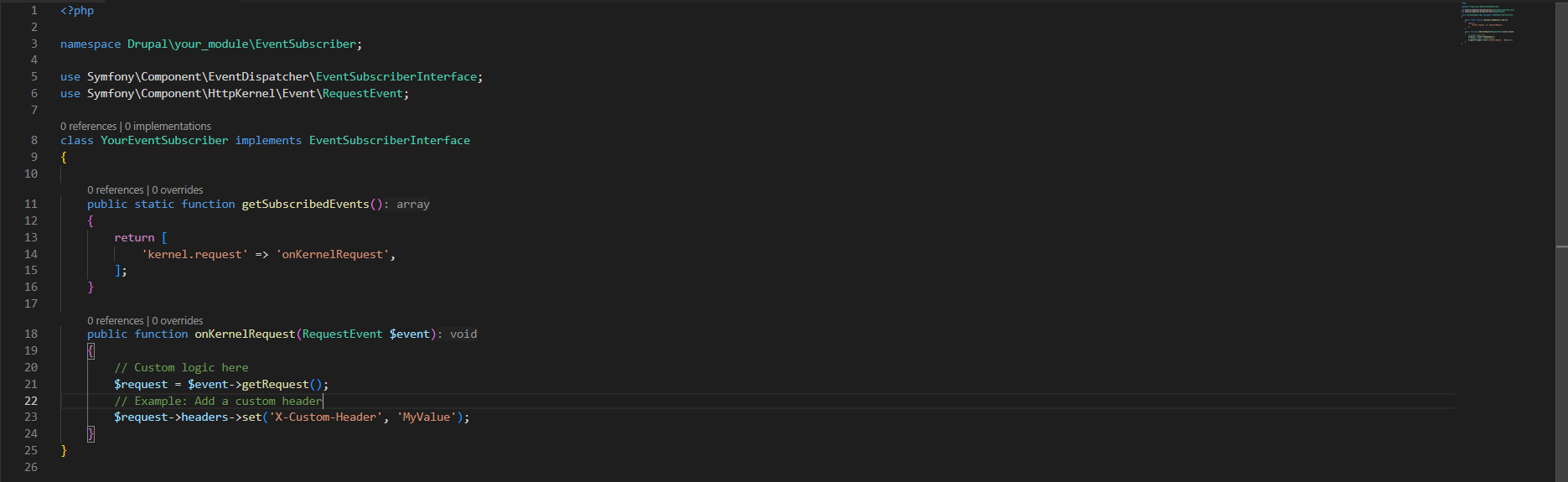
Form definition example (located at sample / src / Form / sampleSettings.php):
namespace Drupal \ sample \ Form;
use Drupal \ Core \ Form \ ConfigFormBase;
use Drupal \ Core \ Form \ FormStateInterface;
/ **
* Settings / Configuration form for the module
* /
class sampleSettings extends ConfigFormBase {
/ **
* {@inheritdoc}
* /
public function getFormId () {
return'sample_settings';
}
/ **
* {@inheritdoc}
* /
protected function getEditableConfigNames () {
return [
'sample_settings.settings',
];
}
/ **
* {@inheritdoc}
* /
public function buildForm (array $ form, FormStateInterface $ form_state) {
$ config = $ this-> config (sample_settings.settings);
$ form ['site_name'] = [
'#type' =>'textfield',
'# title' => $ this-> t ('Enter the site name'),
'# required'=> TRUE,
' # default_value '=> $ config-> get ('site_name'),
];
return parent :: buildForm ($ form, $ form_state);
}
/ **
* {@inheritdoc}
* /
public function submitForm (array & $ form, FormStateInterface $ form_state) {
$ submit_data = $ form_state-> getValues ();
// Retrieve the configuration.
$ This-> config ('custom_fetch_ftp. settings')-> set ('site_name', $ submit_data ['site_name'])-> save ();
parent :: submitForm ($ form, $ form_state);
}
}
In this way we can fetch our configurations anywhere in our Drupal codebase like this
$ config = \ Drupal :: config ('sample_settings.settings');
$ site_name = $ config-> get ('site_name');