Understanding Drupal Configuration
Structured configuration management offers significant benefits, playing a key role in development workflows, team collaboration, and simplified deployment strategies. It enables version control of site settings and facilitates easy rollbacks of changes. This system is crucial for deploying features reliably from development to staging and then to production environments. Without proper management, sites face risks of inconsistency, manual errors, and unreliable deployments. Ultimately, adopting best practices in configuration management improves development workflows, ensures reliable deployments, and enhances team collaboration, building resilient Drupal websites prepared for future updates and integrations.
Troubleshooting Common Configuration Issues
However, challenges can arise. Users may encounter incompatible configuration versions if exporting from one Drupal version or module update and importing into another, as core and module changes can alter configuration schemas. Configuration conflicts occur when imported settings clash with existing ones, requiring careful review, selective imports, manual adjustments, or resetting specific items. Permission errors are also common, where incorrect file system permissions for the config directory prevent successful operations, necessitating adjustment of server permissions to grant the web server write access. Furthermore, managing configuration dependencies is vital; imported configuration often relies on other modules, and Drupal will alert users to missing requirements, demanding that all necessary modules and features are enabled before import. It is always recommended to test imports on a staging environment to prevent disruptions to production sites.
The Drupal Configuration Export and Import Process
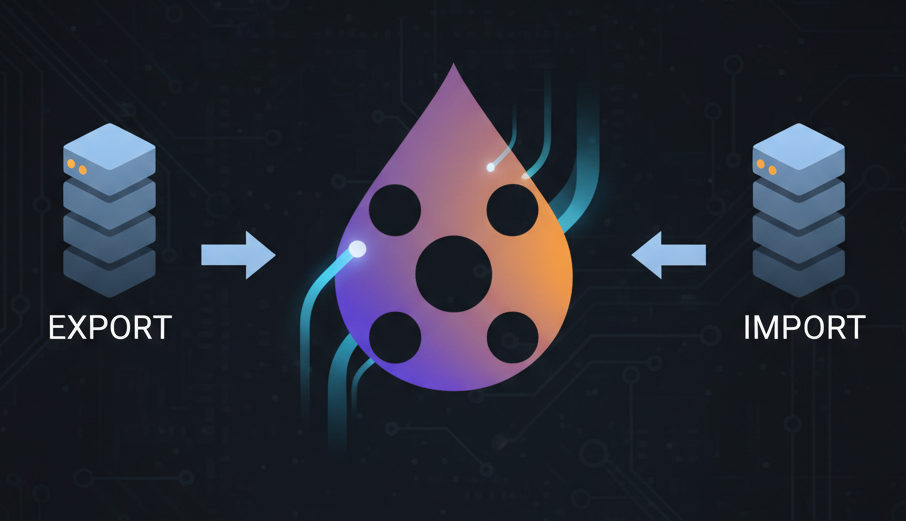
The practical application of configuration management involves both export and import processes. Drupal stores configuration as human-readable YAML files, typically in the config/sync directory, with each file representing a specific configuration item.
To export configuration:
- Full Export (UI): Navigate to /admin/config/development/configuration/full-export and click "Export" to download a compressed archive of all active configuration.
- Full Export (Drush): Use the command drush config:export, which saves all configuration files to the config/sync directory. Regular exports are a recommended development maintenance routine.
- Specific Export (Drush): For targeted development, use commands like drush config:export --module=views to export only view configurations, useful for sharing particular features.
To import configuration:
- Preparation: Before importing, manage exported files carefully. Adjust or exclude environment-specific settings (like database credentials) that differ between environments. Crucially, ensure all necessary modules are enabled to meet dependencies, and always back up your current configuration to protect against data loss.
- Full Import (UI): Go to /admin/config/development/configuration/import, upload a .tar.gz archive, review the proposed changes, and then confirm the import.
- Full Import (Drush): Execute drush config:import to apply changes from files in the config/sync directory to the active configuration, updating or creating existing items.
- Specific Import (Drush): Use commands such as drush config:import --module=views or import a specific YAML file directly for precise control over settings.
Advanced Configuration Management Techniques
For more advanced scenarios, Configuration Splits allow managing environment-specific settings for development, staging, and production within a single project, reducing manual overrides. Integrating with Git for version control tracks all configuration changes, enabling a historical record and best practices like committing changes to Git and deploying updated code and configuration together.
Conclusion
In summary, Drupal configuration export and import are fundamental skills for managing site settings and moving them between environments effectively. While both UI and Drush methods are available, the Drush configuration synchronization process is highly recommended for its speed and efficiency. By using drush config:export to extract changes to the config/sync directory and drush config:import to apply those changes, developers can quickly and reliably synchronize configurations, integrating seamlessly with version control systems and fostering better team collaboration
Bonus: Automating Deployments with CI/CD
To further enhance your configuration management workflow, integrate drush config:import into your Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipeline (e.g., using GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, or Jenkins). This automates deployments, ensuring that every code push with configuration changes is consistently and reliably applied to your staging and production environments, reducing manual error and streamlining the entire development-to-production process.